The Internet of Things (IoT) continued its rapid expansion in 2024, driven by
advancements in smart home technologies, enhanced connectivity and the
evolution of industry standards. Looking ahead, 2025 is poised to bring even
greater innovations, particularly for smart homes and buildings. Here are
seven key trends expected to shape the IoT landscape in 2025.
- AI/ML will rely on wireless to bring intelligence to the edge
The recent advances in AI/ML will bring more intelligence and automation to
our lives than ever before, especially in smart homes and buildings.
However, streaming the massive amounts of data generated by smart devices to
the cloud reduces battery life and increases system reaction time. For many
edge devices, running any portion of the AI/ML locally greatly impacts the
overall system performance. Innovations in hardware, like NXP’s
eIQ Neutron Neural Processing Unit
(NPU) AI accelerator, and in software, like the
eIQ Toolkit
and recent addition of
eIQ Time Series Studio, make edge AI on embedded devices possible. Wireless technologies such as
Wi-Fi and Thread connect these intelligent devices to local networks and the
Internet, enabling cloud connectivity and device-to-device communication.
When combined with Matter, edge devices in 2025 will have seamless
connectivity and interoperability, which will allow the new generation of
AI/ML capabilities to be realized.
-
Interoperability will provide the foundation for intelligent energy
management
Around the world, regulations and efforts to reduce carbon footprints are
driving homes and buildings to become more energy-efficient. Achieving the
next level of energy efficiency requires intelligent energy orchestration,
where the electric grid, home energy generators, storage systems and major
appliances work seamlessly together to optimize overall energy consumption.
For instance, a washing machine could delay starting a load of laundry if
solar panels are not generating enough energy and the grid is under heavy
demand. To enable this level of coordination, appliances, solar energy
systems and smart meters must be interoperable and communicate using a
shared standard. Advances in Matter are bringing this vision closer to
reality in 2025, with NXP’s intelligent system solutions providing
developers with the tools to deliver new levels of energy efficiency to
consumers.
Improving efficiency will require interoperable devices and energy coordination. Learn more about the latest in Matter and energy management.
-
Thread will improve smart home infrastructure as Thread end device adoption
continues to accelerate
Key to enabling a truly autonomous home is the low-power, low data rate mesh
network provided by Thread. Using Thread, devices can last for years on a
single, small battery and have robust connectivity from Thread’s
self-healing mesh network. Built on IPv6, Thread is fully supported by
Matter and complements higher data rate Wi-Fi networks. The latest version
of Thread, version 1.4, adds several enhancements and further accelerates
adoption in 2025. For example, Thread now has a standardized way to share
network credentials with new devices and border routers, allowing them to
all join a single Thread network. Version 1.4 also supports extending Thread
networks using Wi-Fi and Ethernet, making Thread networks even more robust.
These improvements will accelerate Thread's adoption in 2025, allowing more
devices to enter the Matter ecosystem and enabling smart homes to be more
connected, automated and energy efficient.
Improvements in Thread will accelerate adoption in the smart home. Learn more from our Thread Wireless Wednesday post.
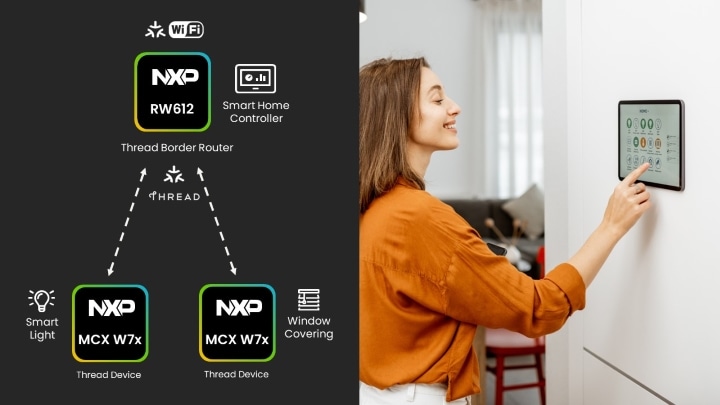 NXP’s wireless MCUs supporting Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Thread and Matter
provide a comprehensive solution from Thread Border Router to Thread End
Device.
NXP’s wireless MCUs supporting Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Thread and Matter
provide a comprehensive solution from Thread Border Router to Thread End
Device.
For a better experience, download the
image.
-
Growth in wireless adoption will make buildings more intelligent, efficient and secure
Not only will wireless connectivity bring new levels of intelligence and
efficiency to homes, it will also play a key role in the evolution of smart
buildings in 2025. Wirelessly connected sensors, thermostats and other IoT
devices will allow existing buildings to be transformed into smart
buildings. Smart buildings will intelligently and efficiently optimize
energy usage, closing window shades when a conference room is empty,
automatically adjusting HVAC usage, and dimming lights based on the outside
light levels. Wireless connectivity, combined with edge intelligence, will
also allow many building systems to be retrofitted with the ability to
predict failures and recommend maintenance to minimize downtime. In
addition, building network security will improve as new systems adopt IP
networking and standardized protocols, such as KNX IoT, that include
multiple layers of security. With these advancements in intelligence,
efficiency and security, the shift toward wirelessly connected smart
buildings will continue to gain momentum throughout 2025.
-
Coexistence will be more important as smart homes and buildings increase the
number of connected devices
The number of connected devices in homes and buildings will continue to
increase exponentially in 2025, with many experts predicting that the
industry will soon ship over 2 billion connected devices each year. This
translates into smart homes and buildings easily having hundreds of
connected devices, often from different manufacturers, that must work
together to deliver a truly autonomous and intelligent home or building. In
the smart home, Matter is helping to realize this vision, by providing a
standard protocol which allows different ecosystems and devices to
seamlessly interact. A Matter-enabled light switch can control a Matter-enabled light bulb, regardless of the manufacturer or ecosystem. Matter also
includes the ability to connect non-Matter smart home devices with bridges,
allowing older devices to join the unified Matter smart home. Likewise, for
buildings, groups like the Connectivity Standards Alliance and KNX
Association, are working to lay the foundation for similar innovation with
connected building systems. These advancements in coexistence will allow the
multitude of smart devices to work together to make homes and buildings
truly intelligent and autonomous.
- Ambient computing will make homes and buildings more autonomous
Ambient computing uses location information to enable a system to make
intelligent, context-aware decisions that would otherwise be impossible. The
ability to determine where a person or object is located within a home or
building enables tremendous potential for automation. For example, a smart
door lock can automatically unlock when it detects that the homeowner is at
the door. In a smart building, a conference room can automatically configure
the lighting, HVAC and IT equipment based on the individuals entering and
the number of occupants. Capabilities such as device ranging to determine
location and ambient sensing to determine motion or presence using a
combination of technologies such as ultrawide band (UWB), Wi-Fi sensing,
and Bluetooth channel sounding, combined with edge processing, form the
basis for ambient computing. In 2025, the growth of smart homes and
buildings along with the release of new application standards like Aliro and
Matter will usher in the era of ambient computing.
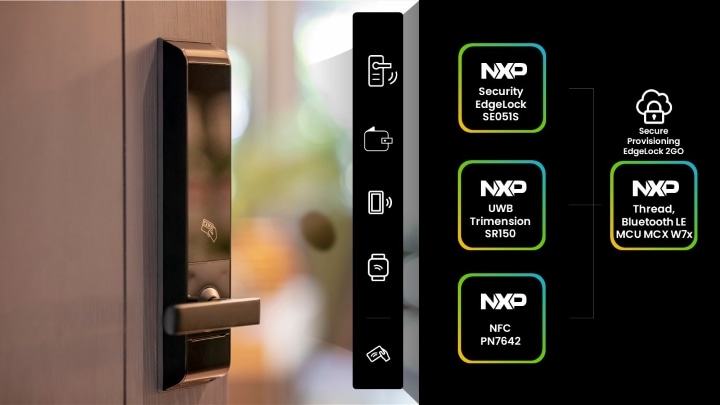 NXP’s ambient computing solutions support technologies such as UWB to bring autonomous systems to the smart home.
NXP’s ambient computing solutions support technologies such as UWB to bring autonomous systems to the smart home.
For a better experience, download the
image.
- The regulations and demands for IoT security will continue to grow
Governments around the world are swiftly enacting new regulations to improve
IoT security and protect consumers. The EU has enacted new legislation,
including the Cyber Resilience Act and Radio Equipment Directive (RED)
updates, to address cybersecurity threats. In the US, the government has
partnered with industry leaders to create the U.S. Cyber Trust Mark.
Consumers are becoming much more security conscious as well, with many
brands now advertising the security of their products. IoT devices for smart
homes and buildings will need to go beyond cryptography and implement system-level security, securing the device, the communications and the network
they operate on. Standards like Matter, Thread and Wi-Fi include multiple
security requirements for the network and communications, while silicon
security, like
NXP’s EdgeLock Secure Enclave, helps implement those requirements and secure the device itself. In 2025,
the requirements for IoT device security will continue to grow, leading
device manufacturers to adopt new standards and technologies to realize
these requirements.