Getting Started with the i.MX 8M Nano EVK Board
Contents of this document
-
Out of the Box
-
Get Software
-
Build, Run
-
MCUXpresso SDK
Sign in to save your progress. Don't have an account? Create one.
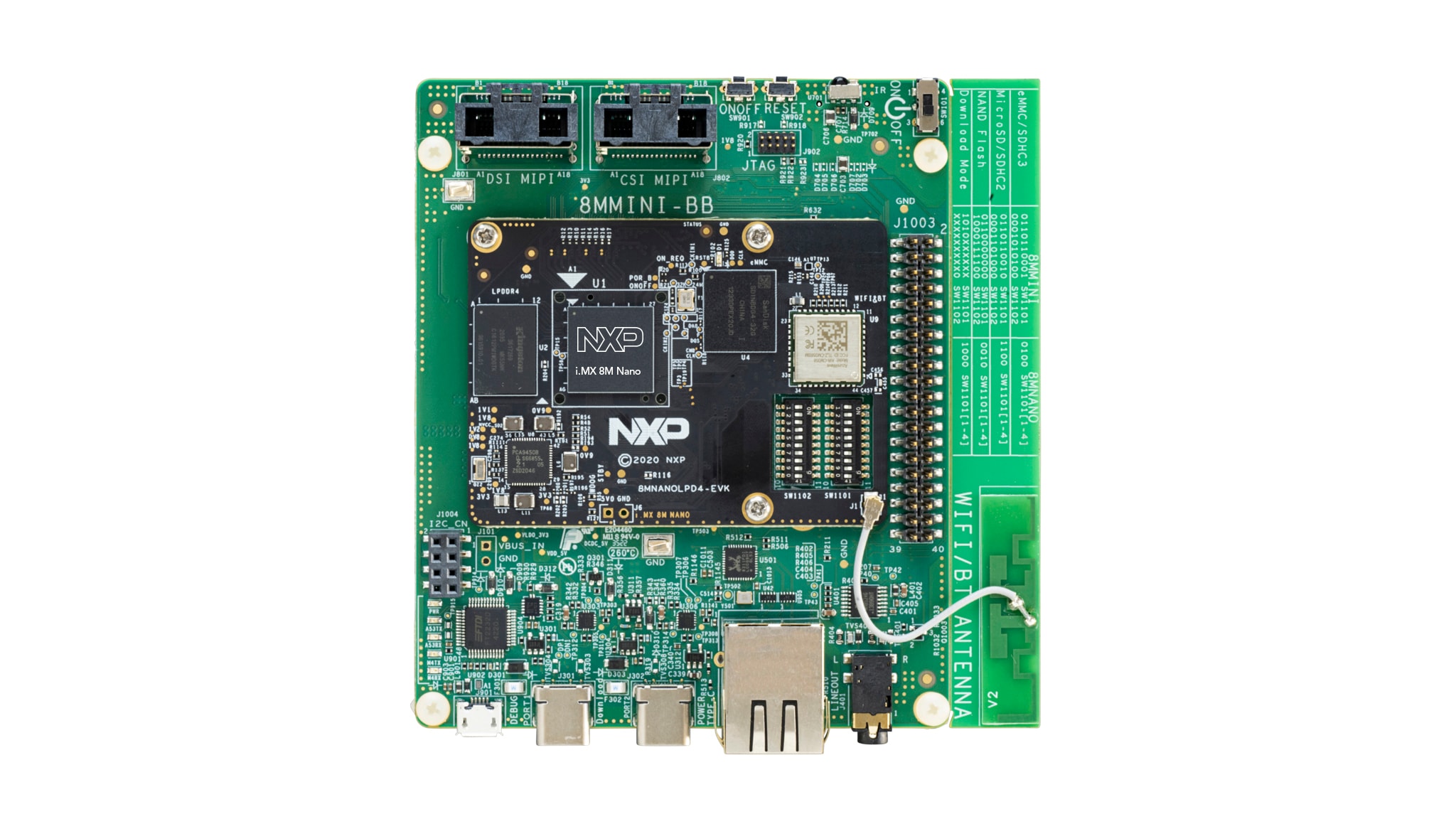
Purchase your i.MX 8M Nano Evaluation Kit
1. Out of the Box
The following section describes the steps to boot the i.MX 8M Nano EVK.
Development kit contains:
- i.MX 8M Nano EVK board for smart devices
- USB cable (micro-B to standard-A)
- USB Type-C Cable – Type-C Male to Type-A Male
- USB Type-C to A Adapter
- USB Type C 45W Power Delivery Supply, 5V/3A; 9V/3A; 15V/3A; 20V/2.25A supported
- IMX-MIPI-HDMI Daughter Card
- Mini-SAS cable
- Quick Start Guide
- Android BSP flashed into the eMMC.
1.1 Get Familiar With the Board
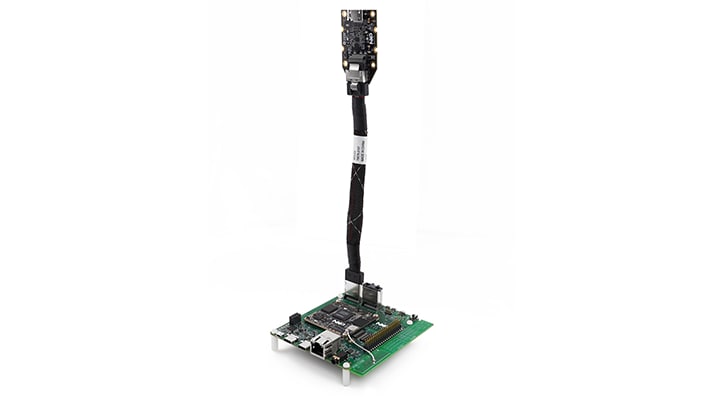
The i.MX 8M Nano EVK kit comes with an IMX-MIPI-HDMI daughter card, which is required to showcase the board's graphical display capabilities.
1.2 Confirm Boot Switches
The boot switches should be set to boot from the eMMC. Only SW1101 [1-4] are used for boot. See table
below.
| Boot Device | SW1101 |
SW1102 |
|---|---|---|
| eMMC/SDHC3 | 0100xxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxx |
The same information can be found on i.MX 8M Nano Reference Manual and on silkscreen on the board near the switches.
1.3 Boot From eMMC
The i.MX 8M Nano EVK comes with a pre-built NXP Android binary demo image flashed on the eMMC. Without modifying the binary inside, booting from the eMMC provides a default system with certain features for building other applications on top of Android.
1.4 Connect USB Debug Cable
Connect the micro-B end of the supplied USB cable into Debug UART port J901. Connect the other end of
the cable to a host computer.
If you are not sure about how to use a terminal application, try one of the following tutorials depending on the operating system of the host machine: Minicom Tutorial, Tera Term Tutorial, PuTTY Tutorial.
1.5 Connect the HDMI Cable
The MIPI-DSI to HDMI accessory card and mini SAS cable are needed for evaluating HDMI.
Connect the mini-SAS cable to J801 on the EVK (MIPI DSI Connector). Connect the other end of
mini-SAS cable to J5 on the MIPI to HDMI accessory card. See below picture for reference.
1.6 Boot Switch Setup
The boot sequence is detailed in the i.MX 8M Nano Reference Manual. In short, the boot modes of the i.MX boards are controlled by the boot configuration switches.
The switches set the boot media (depending on board, i.e. SD card, eMMC, NAND), the serial download protocol mode (SDP) or the value set on eFuses.
The SDP is also the fallback for the boot media, in other words, when the switches are configured to boot from SD card but the SD card slot is empty, or the SD card binary content is not bootable, the boot sequence continues to the SDP boot. 8
The following table lists the boot switch settings on the i.MX 8M Nano EVK board. The same information can be found on i.MX 8M Nano Reference Manual and on silkscreen on the board near the switches.
| Boot Media | SW1101 [D1-D10] |
SW1102 [D1-D10] |
|---|---|---|
| eMMC/SDHC3 | 0100xxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxx |
| MicroSD/SDHC2 | 1100xxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxx |
| NAND Flash | 0010xxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxx |
| SDP | 1000xxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxx |
1.7 Connect Power Supply
Connect the power supply cable to the power connector (J302).
Power the board by flipping the switch (SW101).
The processor starts executing from the on-chip ROM code. With the default boot switch setup, the code reads the fuses to define the media where it is expected to have a bootable image. After it finds a bootable image, the U-Boot execution should begin automatically.
Information is printed in the serial console for the Cortex®-A53. If you do not stop the U-Boot process, it continues to boot the kernel.
1.8 Congratulations Android Has Booted
During the boot process, you will see 4 penguins appear in the upper left-hand corner of the HDMI display. You will then see the Android logo and the Android desktop can be seen after the boot process is finished. You can start operating with the mouse. Connect the mouse to J301 (USB Type-C Port1) through the USB Type-C to A adapter that is provided in the box.
2. Get Software
This section is applicable ONLY if attempting to load a Linux operating system on the board.
The i.MX Linux Board Support Package (BSP) is a collection of binary files, source code, and support files that are used to boot an Embedded Linux image on a specific i.MX development platform.
Current releases of Linux binary demo files can be found on the i.MX Linux download page. Additional documentation is available in the i.MX Linux documentation bundle under the Linux sections of the i.MX Software and Development Tool.
2.1 Overview
Before the Linux OS kernel can boot on an i.MX board, the Linux kernel is loaded to a boot device (SD card, eMMC, and so on) and the boot switches are set to boot that device.
There are various ways to download the Linux BSP image for different boards and boot devices.
For this getting started guide, only a few methods to transfer the Linux BSP image to an SD card are listed. Experienced Linux developers can explore other options.
2.2 Download an NXP Linux BSP Pre-Built Image
The latest pre-built images for the i.MX 8M Nano EVK are available on the Linux download page under the most current version on Linux.
The pre-built NXP Linux binary demo image provides a typical system and basic set of features for using and evaluating the processor. Without modifying the system, the users can evaluate hardware interfaces, test SoC features, and run user space applications.
The pre-built NXP Linux binary demo image provides a typical system and basic set of features for using and evaluating the processor. Without modifying the system, the users can evaluate hardware interfaces, test SoC features, and run user space applications.
When more flexibility is desired, an SD card can be loaded with individual components (boot loader, kernel, dtb file, and rootfs file) one-by-one or the .sdcard image is loaded and the individual parts are overwritten with the specific components.
2.3 Burn NXP Linux BSP Image Using Universal Update Utility (UUU)
The latest pre-built images for the i.MX 8M Nano EVK are available on the Linux download page under the most current version on Linux.
The pre-built NXP Linux binary demo image provides a typical system and basic set of features for using and evaluating the processor. Without modifying the system, the users can evaluate hardware interfaces, test SoC features, and run user space applications.
The pre-built NXP Linux binary demo image provides a typical system and basic set of features for using and evaluating the processor. Without modifying the system, the users can evaluate hardware interfaces, test SoC features, and run user space applications.
When more flexibility is desired, an SD card can be loaded with individual components (boot loader, kernel, dtb file, and rootfs file) one-by-one or the .sdcard image is loaded and the individual parts are overwritten with the specific components.
Linux®
Install UUU on Linux Distro
Download the latest stable files from UUU GitHub page . An extensive tutorial for UUU can be found in UUU GitHub page .
uuulibusb1(via apt-get or any other package manager)
Burn the NXP Linux BSP Image to the Board
By default, this procedure flashes the image to the SD card flash. Check the UUU GitHub page for reference on how to flash the image to other devices.
Open a terminal application and change directory to the location where uuu and the latest Linux distribution for i.MX 8M Nano EVK are located. Add execution permission to the uuu file and execute it. uuu waits for the USB device to connect
1$ chmod a+x uuu $ sudo ./uuu kernel_version_images_SOC.zipTurn on the board, uuu starts to copy the images to the board.
When it finishes, turn off the board, and consult Boot switch setup to configure the board to boot from SD card.
Windows™
Install UUU on Windows
Download the latest stable files from UUU GitHub page . An extensive tutorial for UUU can be found in UUU GitHub page.
uuu.exe- Serial USB drivers (depending on your board and Windows installation - check Windows Device Manager).
Burn the NXP Linux BSP image to the board
By default, this procedure flashes the image to the SD card flash. Check the UUU GitHub page for reference on how to flash the image to other devices.
Open the command prompt application and navigate to the directory where the uuu.exe file and the Linux release for the i.MX 8M Nano EVK are located.
1uuu.exe kernel_version_imagesSOC.zipTurn on the board, uuu starts to copy the images to the board.
When it finishes, turn off the board, and consult Boot switch setup to configure the board to boot from SD card.
3. Build, Run
3.1 Android™
This section describes the boot process of loading the i.MX 8M Nano EVK board with an Embedded Android system image and introduces how to build the software components that create your own system image. For details on building the Android platform, see Building Android .
The current release includes Demo Images, Source code and Documentation. These can also be found in Android OS for i.MX Applications Processor.
3.2 Overview
The storage devices on the development system (MMC/SD or NAND) must be programmed with the U-Boot boot loader. The boot process determines which storage device to access based on the switch settings. When the boot loader is loaded and begins execution, the U-Boot environment space is then read to determine how to proceed with the boot process.
-
- U-Boot image:
u-boot.imx - boot image:
boot.img - Android system root image:
system.img - Recovery root image:
recovery.img
- U-Boot image:
The images can come from pre-built release packages or be created from source code. Regardless of how you obtain them, all Android images contain the following components:
For more information about the Android BSP refer to the Android User Guide .
3.3 Download NXP Android BSP Image
The pre-built NXP Android demo image provides a default system with certain features for evaluation. Without modifying the system, users can perform some basic operations and interact with the system to test hardware interfaces and develop software application in the user space.
The pre-built images from the package are categorized by boot device and put in the directory with the device name. The latest pre-built image files can be found in Android section on the i.MX Software and Development Tool or on the demo images downloader link.
3.4 Burn NXP Android BSP Image Using UUU
In addition to the connections from Out of box chapter, connect the J301 to the host machine using the proper USB cable and turn off the board.
Consult the Boot Switch Setup and configure the board to boot on SDP (Serial Download Protocol) mode.
Depending on the OS used in the host machine, the way to transfer the Android BSP image onto an SD card can vary.
4. MCUXpresso SDK
The MCUXpresso Software Development Kit (MCUXpresso SDK) provides comprehensive software source code to be executed in the i.MX 8M Nano M7 core. If you do not wish to enable the Cortex®-M7 on i.MX 8M Nano at this moment you can skip this section.
4.1 Overview
The MCUXpresso SDK is designed for the development of embedded applications for Cortex®-M7 standalone or collaborative use with the A cores. Along with the peripheral drivers, the MCUXpresso SDK provides an extensive and rich set of example applications covering everything from basic peripheral use case examples to demo applications. The MCUXpresso SDK also contains RTOS kernels and device stack and various other middleware to support rapid development.
This guide shows how to run the hello_world.bin demo provided by the REL_2.9.0 release. For detailed information on MCUXpresso SDK and how to build and deploy custom demos, please see the MCUXpresso SDK site.
4.2 Run Applications Using U-Boot
This section describes how to run applications using an SD card and pre-built U-Boot image for i.MX processor.
- Following the steps from section 2—Embedded Linux of this Getting Started guide, prepare an SD card with a pre-built U-Boot + Linux image from the Linux BSP package for the i.MX 8M Nano processor. If you have already loaded the SD card with a Linux image, you can skip this step
- Insert the SD card in the host computer (Linux or Windows) and copy the application image (for example hello_world.bin) to the FAT partition of the SD card
- Safely remove the SD card from the PC
- Insert the SD card to the target board. Make sure to use the default boot SD slot and double check the Consult the Boot Switch Setup
-
Connect the DEBUG UART connector on the board to the PC through USB cable. The Windows OS installs the USB driver automatically, and the Ubuntu OS will find the serial devices as well.
See Connect USB debug cable section in Out of box for more instructions on serial communication applications
- Open a second terminal on the i.MX 8M Nano EVK board's second enumerated serial port. This is the Cortex®-M7's serial console. Set the speed to 115200 bit/s, data bits 8, 1 stop bit (115200, 8N1), no parity
-
Power up the board and stop the boot process by pressing any key before the U-Boot countdown reaches zero. At the U-Boot prompt on the first terminal, type the following commands
1
=> fatload mmc 0:1 0x48000000 hello_world.bin => cp.b 0x48000000 0x7e0000 0x20000 => bootaux 0x7e0000
These commands copy the image file from the first partition of the SD card into the Cortex-M7's TCM and releases the Cortex-M7 from reset.
Security and Integrity
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| AN12714 i.MX Encrypted Storage Using CAAM Secure Keys | Provides the steps to run a transparent storage encryption at block level using DM-Crypt taking advantage of the secure key feature provided by i.MX's Cryptographic Accelerator and Assurance Module (CAAM). |
| AN12632 Enhanced OpenSSL on i.MX 8M and i.MX 8MM | This application note describes how to add support for accelerated OP-TEE OS with Cryptographic Accelerator and Assurance Module (CAAM) on top of OpenSSL. The final result being an enhanced OpenSSL capable of accelerating crypto algorithms in a secure way via OP-TEE. |
| Trusted Execution Environment: Getting Started with OP-TEE on i.MX Processors | An overview of TEE, example use cases and how to leverage i.MX hardware security features from OP-TEE. |
| AN12838 Strengthening Public Key Cryptography using CAAM Secure Key | Describes the public key cryptography scheme based on the Black Key feature provided by the i.MX application processors. |
| Secure the Edge: Manufacturing Protection: Provision Sensitive Material in an Unsecure Environment | This webinar will provide an introduction to the Manufacturing protection feature and discuss how it can be used to ensure that sensitive material is delivered and installed securely. |
| Steps to Enable Secure Boot in i.MX8M Nano | Step-by-step process including generating a PKI tree, SRK table and how to sign and securely boot a bootloader image. |
CAAM Module Example
The i.MX 8M Nano EVK board includes the Cryptographic Acceleration and Assurance Module (CAAM) module that can be used through CryptoDev in order to accelerate by hardware the encryption and decryption process. It is recommended to use this module when working with large amounts of data or in any application where performance is important.
Checking the Speed Performance
OpenSSL is an open source project that defines the security protocols SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security). It has a software library that can be used in applications that requires a secure information transmission in order to prevent eavesdropping.
OpenSSL includes a speed command that tests the encryption performance for a
desired encryption algorithm. For this example, the algorithm used is the
aes-128-cbc that implements the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm, with a Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) mode of operation and 128 bits block.
The OpenSSL speed test can be seen using the following command:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223# openssl speed -evp aes-128-cbc
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 16 size blocks: 43389139 aes-128-cbc's in 2.99s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 64 size blocks: 28788614 aes-128-cbc's in 3.00s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 256 size blocks: 11766741 aes-128-cbc's in 2.99s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 1024 size blocks: 3674139 aes-128-cbc's in 2.99s
Doing aes-128-cbc for 3s on 8192 size blocks: 495157 aes-128-cbc's in 3.00s
OpenSSL 1.0.2p 14 Aug 2018
built on: reproducible build, date unspecified
options:bn(64,64) rc4(ptr,char) des(idx,cisc,16,int) aes(partial) idea(int) blowfish(ptr)
compiler: arm-poky-linux-gnueabi-gcc -march=armv7ve -mfpu=neon -mfloat-abi=hard -mcpu=cortex-a7 -DL_ENDIAN -DTERMIO -O2 -pipe -g -feliminate-unused-debug-types -Wall -Wa,--noexecstack -DHAVE_CRYPTODEV -DUSE_CRYPTODEV_DIGESTS
The 'numbers' are in 1000s of bytes per second processed. type 16 bytes 64 bytes 256 bytes 1024 bytes 8192 bytes
Aes-128-cbc 193627.86k 513839.78k 837089.96k 1048974.64k 1130986.42kSolution: In doc “AN12838 Strengthening Public Key Crptography using CAAM Secure Key” section 5.2.1 and 5.2.2. it describes details of the usage.
Tools and References
Security Reference Manual for i.MX 8M Nano Applications Processor.
Wired Communications
Wired Communications
With Linux running on the i.MX board, you can evaluate special features that i.MX SoCs provide. This tutorial shows the step-by-step instructions on how to connect to the Internet on Linux with i.MX 8M Nano EVK:
- Connect an Ethernet cable to the board
RJ-45connector - Log in
- Boot up the board and wait for the Linux prompt
- At the Linux prompt, enter the following command
- Ping any site to corroborate functionality
1# ifconfig eth0123456789# ping 8.8.8.8 PING 8.8.8.8 (8.8.8.8) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=119 time=4.81 ms 64 bytes
from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=2 ttl=119 time=4.87 ms 64 bytes
from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=3 ttl=119 time=4.94 ms 64 bytes
from 8.8.8.8: icmp_seq=4 ttl=119 time=4.61 msWireless Connectivity
Wireless Connectivity
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Connectivity | Integrated support for cloud services including Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud IoT. |
Power Management
Power management includes device-specific techniques and information on power management and low-power optimization.
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| AN12778 i.MX 8M Nano Power Consumption Measurement | Illustrates the current drain measurements of the i.MX 8M Nano application processors taken on the NXP EVK platform through several use cases. |
| AN12225 How to Reduce SoC Power when Running M4 with A53 on i.MX8M | With AMP applications a user may find a VDD_SOC current that is much higher than expected. This document discusses the root cause and solution. |
| M4 Low Power Demo on i.MX 8MM | Allows you to test power consumption on the i.MX 8M EVKs. |
Low Power Mode Suspension Example
With Linux running on the i.MX board, you can evaluate special features that i.MX SoCs provide. This example shows how to suspend to low-power modes and resume to normal operation.
Enter the command below in order to enable serial TTY as a wake up source for the board:
Path:
1# echo enabled > /sys/class/tty/ttymxc0/power/wakeupEnter the command below to enter Suspend-To-RAM mode:
1# echo mem > /sys/power/state PM: suspend entry (deep) PM: Syncing filesystems ... done. Freezing user space processes ... (elapsed 0.001 seconds) done. OOM killer disabled. Freezing remaining freezable tasks ... (elapsed 0.000 seconds) done. Suspending console(s) (use no_console_suspend to debug)Press the SW901 switch to wake-up the board. The following messages should appear on terminal:
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859HIFsuspendwow TODO
PM: suspend devices took 0.112 seconds
Disabling non-boot CPUs ...
CPU1: shutdown
psci: CPU1 killed.
CPU2: shutdown
psci: CPU2 killed.
CPU3: shutdown
psci: Retrying again to check for CPU kill
psci: CPU3 killed.
Enabling non-boot CPUs ...
Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU1
GICv3: CPU1: found redistributor 1 region 0:0x00000000388a0000
CPU1: Booted secondary processor [410fd034]
cache: parent cpu1 should not be sleeping
CPU1 is up
Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU2
GICv3: CPU2: found redistributor 2 region 0:0x00000000388c0000
CPU2: Booted secondary processor [410fd034]
cache: parent cpu2 should not be sleeping
CPU2 is up
Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU3
GICv3: CPU3: found redistributor 3 region 0:0x00000000388e0000
CPU3: Booted secondary processor [410fd034]
cache: parent cpu3 should not be sleeping
CPU3 is up
PM: resume devices took 0.028 seconds
OOM killer enabled.
Restarting tasks ... done.
PM: suspend exit Audio
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| DSP Concepts offering for i.MX 8 Processors | Learn about audio platform offerings from DSP Concepts for the i.MX 8M family. |
Tools and References
i.MX Audio Board Hardware User's Guide. This manual includes system setup and configurations and provides detailed information on the usage of the i.MX Audio Board System from a hardware perspective.
Simple Audio Example
Connect your earphone to the Audio Jack on the i.MX 8M Nano EVK board.
If your earphone includes a microphone feature (TRRS with four contacts), do not push the microphone jack to the end. Leave one contact ring outside.
1234567891011121314151617181920212223#aplay -1
**** List of PLAYBACK Hardware Devices ****
card 0: imxspdif [imx-spdif], device 0: S/PDIF PCM snd-soc-dummy-dai-0 [S/PDIF PCM snd-soc-dummy-dai-0]
Subdevices: 1/1
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
card 2: wm8524audio [wm8524-audio], device 0: HiFi wm8524-hifi-0
[]
Subdevices: 1/1
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
card 2: wm8524audio [wm8524-audio], device 1: HiFi-ASRC-FE (*)
[]
Subdevices: 1/1
Subdevice #0: subdevice #0
# gst-launch-1.0 audiotestsrc ! alsasink device=plughw:2
Setting pipeline to PAUSED ...
Pipeline is PREROLLING ...
Redistribute latency...
Pipeline is PREROLLED ...
Setting pipeline to PLAYING ...
New clock: GetAudioSinkClockYou should be able to listen to a tone on the earphone.
When you are done with the tone, finish the command line by pressing kbd: [Ctrl+C]
This simple example shows the link between audiotestsrc and alsasink.
Connect your earphone to the Audio Jack on the i.MX 8M Nano EVK board.
Decoder Video Audio Example
This example explains how to decode just the audio from a video file. Copy a video file to your /home/root/ on your SD card roots partition, boot the board from the SD card and run the command below:
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879808182838485868788899091# gplay-1.0 SampleVideo_1280x720_2mb.mp4
FSL_GPLAY2_01.00_LINUX build on Mar 12 2018 11:48:19
Set VideoSink kmssink
Set TextSink fakesink ====== AIUR: 4.3.4 build on Mar 12 2018 11:47:35. ======
Core: AVI_PARSER_03.05.29 build on Aug 31 2017 09:15:57
file: /usr/lib/imx-mm/parser/lib_avi_parser_arm_elinux.so.3.1
Track 00 [video]: Disabled
Codec: 4, SubCodec: 1
-----------------------
------------------------ Track 01 [audio_0] Enabled
Duration: 0:09:56.424000000
Language: und
Mime: audio/mpeg, mpegversion=(int)1, channels=(int)2, rate=(int)48000, bitrate=(int)0
codec_data=(buffer)014d401fffe10017674d401fda014016ec0440000003004000000c83c60ca801000468ef3c80
------------------------
====== BEEP: 4.3.4 build on Mar 12 2018 11:47:45. ======
Core: MP3 decoder Wrapper build on Jan 11 2018 10:20:25
file: /usr/lib/imx-mm/audio-codec/wrap/lib_mp3d_wrap_arm_elinux.so.3
CODEC: BLN_MAD-MMCODECS_MP3D_ARM_02.13.01_ARMV8 build on Jan 11 2018 10:05:45. [Stop (No Repeated)][Vol=1.0][00:00:00/00:09:56]=========== fsl_player_play()=========== FSL_GPLAY2_01.00_LINUX build on Mar 12 2018 11:48:19
[h]display the operation Help
[p]Play
[s]Stop
[e]Seek
[a]Pause when playing, play when paused
[v]Volume
[m]Switch to mute or not
[>]Play next file
[ [r]Switch to repeated mode or not
[u]Select the video track
[d]Select the audio track
[b]Select the subtitle track
[f]Set full screen
[z]resize the width and height
[t]Rotate
[c]Setting play rate
[i]Display the metadata
[x]eXit
State changed: buffering
State changed: playing
[Playing (No Repeated)][Vol =1.0][00:00:13/00:00:13]EOS Found
getNextItem No next item!
No more media file, exit gplay!
State changed: stopped
Exit display thread
FSL_PLAYER_UI_MSG_EXIT
fsl_player_deinitDecoder Video Audio Example
This example explains how to decode just the audio from a video file. Copy a video file to
your /home/root/ on your SD card roots partition, boot the board from the SD
card and run the command below:
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879808182838485868788899091# gplay-1.0 SampleVideo_1280x720_2mb.mp4
FSL_GPLAY2_01.00_LINUX build on Mar 12 2018 11:48:19
Set VideoSink kmssink
Set TextSink fakesink ====== AIUR: 4.3.4 build on Mar 12 2018 11:47:35. ======
Core: AVI_PARSER_03.05.29 build on Aug 31 2017 09:15:57
file: /usr/lib/imx-mm/parser/lib_avi_parser_arm_elinux.so.3.1
Track 00 [video]: Disabled
Codec: 4, SubCodec: 1
-----------------------
------------------------ Track 01 [audio_0] Enabled
Duration: 0:09:56.424000000
Language: und
Mime: audio/mpeg, mpegversion=(int)1, channels=(int)2, rate=(int)48000, bitrate=(int)0
codec_data=(buffer)014d401fffe10017674d401fda014016ec0440000003004000000c83c60ca801000468ef3c80
------------------------
====== BEEP: 4.3.4 build on Mar 12 2018 11:47:45. ======
Core: MP3 decoder Wrapper build on Jan 11 2018 10:20:25
file: /usr/lib/imx-mm/audio-codec/wrap/lib_mp3d_wrap_arm_elinux.so.3
CODEC: BLN_MAD-MMCODECS_MP3D_ARM_02.13.01_ARMV8 build on Jan 11 2018 10:05:45. [Stop (No Repeated)][Vol=1.0][00:00:00/00:09:56]=========== fsl_player_play()=========== FSL_GPLAY2_01.00_LINUX build on Mar 12 2018 11:48:19
[h]display the operation Help
[p]Play
[s]Stop
[e]Seek
[a]Pause when playing, play when paused
[v]Volume
[m]Switch to mute or not
[>]Play next file
[ [r]Switch to repeated mode or not
[u]Select the video track
[d]Select the audio track
[b]Select the subtitle track
[f]Set full screen
[z]resize the width and height
[t]Rotate
[c]Setting play rate
[i]Display the metadata
[x]eXit
State changed: buffering
State changed: playing
[Playing (No Repeated)][Vol =1.0][00:00:13/00:00:13]EOS Found
getNextItem No next item!
No more media file, exit gplay!
State changed: stopped
Exit display thread
FSL_PLAYER_UI_MSG_EXIT
fsl_player_deinitDisplay and Graphics
Display and Graphics
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| i.MX Graphics User’s Guide | Provides information on graphic APIs and driver support for developers writing graphics applications or video drivers. |
| i.MX 8 Gstreamer User Guide | Learn more about how to use GStreamer version 1.0 on the i.MX 8M Nano EVK. Includes examples for decode, encode, camera, video composition and video scaling and rotation. |
| Achieve Exceptional Graphics for IoT Devices of Tomorrow with NXP’s i.MX 8M Nano Applications Processor Webinar | Provides an overview of the i.MX 8M Nano and how Crank Software’s Storyboard differs from traditional UI development tools. |
| Setting i.MX 8M Mini and Nano MIPI-DPHY Clock | How to calculate necessary timing parameters. |
| Implementing Graphics in Real-time Industrial HMI Systems with NXP MCUs and Embedded Wizard | NXP has partnered with TARA Systems to offer Embedded Wizard as an Enabling Software Technology. |
Camera Interfaces
Camera Interfaces
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| i.MX 8 Camera Use Cases | Learn more about the i.MX 8 MIPI CSI use case, Advanced Gstreamer camera use cases, available cameras and daughter cards supported by the i.MX 8M Nano EVKB, compatible Device Tree (DTS) files, and how to enable different camera options. |
| i.MX 8 GStreamer User's Guide | User guide for the GStreamer version 1.0 based accelerated solution included in all the i.MX 8 family SoCs supported by NXP BSP L5.4.24_1.1.0. |
Machine Learning
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) typically encompasses applications where classification, recognition and prediction of man-made abstractions are desired. Examples include Image Recognition, Gesture Recognition, Anomaly Detection, Speech-to-Text, Text-to-Speech, ASR, Scene Recognition and many more. This section will focus specifically on the NXP ML tools applied to image or video streams. The audio section may reference the included examples.
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| eIQ® ML Software Development Environment | Enables the use of ML algorithms on NXP MCUs, i.MX RT crossover MCUs, and i.MX family SoCs. eIQ software includes inference engines, neural network compilers and optimized libraries. |
| i.MX Machine Learning User's Guide | The NXP eIQ UM for i.MX toolkit provides a set of libraries and development tools for machine learning applications targeting NXP microcontrollers and application processors. |
| eIQ Fact Sheet | Machine learning software for NXP i.MX and MCUs - libraries, example applications and inference engines. |
| AN13001 Glow Memory Analysis | How to understand the Glow memory information generated by the Glow compiler and calculate the memory required for a particular model. This compiler can then be used to determine the minimum memory size that is needed to run the model. |
| AN12766 Anomaly Detection with eIQ using K-Means clustering in Tensor Flow Lite | Step by step instruction to enable a machine condition monitoring application using anomaly detection. |
| Getting Started with eIQ Software for i.MX Applications Processors | A series of step-by-step tutorials using our eIQ ML software development environment from unboxing a board, to deploying, to modeling, to inferencing at the edge. |
Device Management and Secure OTA
Device Management and Secure OTA
| Documents and Videos | Description |
|---|---|
| AN12900 Secure Over-the-Air Prototype for Linux Using CAAM and Mender or SW Update | Provides a prototype implementation for Secure OTA for Linux images, specifically for the i.MX 8M/MM. |
| AN12921 Google Cast Authentication Aspects Implementation on i.MX | This app note provides details about security properties required for Google Voice Assistant (GVA) and Cast for Audio (C4A) on the security aspects and their implementations on NXP's GVA/C4A reference platform. |
| Docker On i.MX8MM with Ubuntu | This document describes a way to create ubuntu rootfson host pc and install docker for any ARM 64 platform. |
Minicom Tutorial
Serial Communication Console Setup
On the command prompt of the Linux host machine, run the following command to determine the port number:
1$ ls /dev/ttyUSB*The smaller number is for Arm® Cortex®-A53 core and the bigger number is for Arm® Cortex®-M7 core.
Minicom Tutorial
Use the following commands to install and run the serial communication program (minicom
as an example):
- Install Minicom using Ubuntu package manager.
1
$ sudo apt-get install minicom - Launch Minicom using a console window using the port number determined earlier.
1
$ sudo minicom /dev/ttyUSB* -s - Configure Minicom as show in Figure 3
- The next step is to connect the HDMI cable

Tera Term Tutorial
Serial Communication Console Setup
The FTDI USB-serial chip on i.MX 8M Mini enumerates two serial ports. Assume that the ports are
COM9 and COM10. The smaller numbered port ( COM9) is for the serial console communication from Arm® Cortex®-A53 and the larger numbered port (COM10) is for Arm® Cortex®-M7 core. The serial-to-USB drivers are available at
FTDI Chip Drivers .
Tera Term Tutorial
Is an open source terminal emulation application. This program displays the information sent from the NXP development platform's virtual serial port.
- Download Tera Term. After the download, run the installer and then return to this webpage to continue
- Launch TeraTerm. The first time it launches, it shows the following dialog. Select the serial option. Assuming your board is plugged in, there should be a COM port automatically populated in the list
- Configure the serial port settings (using the
COMport number identified earlier) to115200baud rate,8data bits, no parity, and1stop bit. To do this, go to Set up → Serial Port and change the settings - Verify that the connection is open. If connected, Tera Term shows something like below in its title bar
- The next step is to connect the HDMI cable

PuTTY Tutorial
Serial Communication Console Setup
The FTDI USB-serial chip on i.MX 8M Mini enumerates two serial ports. Assume that the ports are
COM9. This represents the serial console communication from Arm® Cortex®-A53 core. The serial-to-USB drivers are available at
FTDI Chip Drivers .
PuTTY Tutorial
PuTTY is a popular terminal emulation application. This program displays the information sent from the NXP development platform’s virtual serial port.
- Download PuTTY After the download, run the installer and then return to this webpage to continue
- Launch PuTTY by either double-clicking on the executable file you downloaded or from the Start menu, depending on the type of download you selected
- Configure In the window that launches. Select the Serial radio button and enter the
COMport number that you determined earlier. Also enter the baud rate, in this case115200 - Click Open to open the serial connection. Assuming the board is connected and you entered the correct
COMport, the terminal window opens. If the configuration is not correct, PuTTY alerts you - The next step is to connect the HDMI cable
Support
Training
To learn what to do next, find your issue below. If you still need help, contact NXP Support.
| Training | Description |
|---|---|
| Meet the i.MX 8M Nano Webinar | Learn more about the differentiating features, target applications and ecosystem of the i.MX 8M Nano family. |
| i.MX 8M Training | Full list of on-demand training, how-to videos and webinars from NXP about this product. |
Forums
Connect with other engineers and get expert advice on designing with the i.MX 8M Nano on one of our community sites.
Product Forums:
- i.MX Forums
- Useful Documents and Threads of i.MX Processors
- i.MX Graphics
- i.MX Solutions
- i.MX8 Coral Development Kit
- Power Management
- Wireless Connectivity
Software Forums:
On this page
- 1.1
Get Familiar With the Board
- 1.2
Confirm Boot Switches
- 1.3
Boot From eMMC
- 1.4
Connect USB Debug Cable
- 1.5
Connect the HDMI Cable
- 1.6
Boot Switch Setup
- 1.7
Connect Power Supply
- 1.8
Congratulations Android Has Booted




