Bluetooth® Low Energy (BLE), with its cost-effective, low-power infrastructure and its ubiquitous
availability in smartphones, has become an important tool for car makers. Over
the past several years, what started as a way to give drivers a better way to
make voice calls, send texts and stream music, has penetrated deeper into the
vehicle architecture, serving to replace legacy technologies, increase
efficiency and add convenience.
For example, BLE can be used as an alternative to traditional LIN and CAN
networks, replacing heavy cables with wireless connectivity. In hybrid and
all-electric vehicles, BLE can be used to send temperature and voltage data
from battery packs to the main vehicle computer, as a part of battery management
systems. In the infotainment system, BLE can increase efficiency by using
duty cycling to put other, more power-intensive communication formats—such as
cellular or Wi-Fi—in sleep mode when not in use. BLE also gives tire pressure
monitoring systems (TPMS) the ability to send notifications to your smartphone
when the tires need air and cand lets you check tire pressure using an app
instead of fiddling with a mechanical gauge.
BLE for Smart Car Access
Of the many ways that BLE can benefit automotive, few promise to improve the
end-user experience more than BLE’s integration into smart access systems,
where a BLE-enabled key fob or smartphone enables handsfree control of the
car’s door locks and ignition along with digital-key car sharing capability.
Handsfree access has been around for a while, but newer formats, based on a
combination of BLE and
ultra-wideband (UWB)
, are much more secure and far less vulnerable to the relay attacks that have
plagued earlier versions of remote access.
These newly defined digital keys go beyond traditional key fobs, extending the
usual features of locking and unlocking the car, opening the windows or
starting the engine, to provide full control over the access rights to the
car. Vehicle owners can share access among family and friends, no matter the
physical distance, and can grant certain rights, ranging from access only to
the car’s trunk to full driving capability. Using wireless protocols such as
BLE and UWB for localization, digital key standards let you access your car
without having to fish your phone out of your pocket or bag, and without
having to open an app. Presence alone is all that’s needed to unlock or lock
doors and start the engine.
The
Car Connectivity Consortium (CCC), for example, is a cross-industry organization, focused on
smartphone-to-car connectivity solutions, that has defined a standard that
enables mobile devices to securely store, authenticate and share digital keys
for vehicles. The CCC’s Digital Key release 3.0 specification, released in
2021, adds BLE and UWB functional requirements for secure car access (NXP is a
CCC board member and helped define the Digital Key 3.0 specification).
Beyond the CCC, other standard bodies, such the Asia-Pacific Connected
Vehicles Industry Association (ICCE) and the Smart Car Association Open
Alliance (ICCOA), have proposed digital-key standards that use a combination
of BLE and UWB.
Taking Automotive BLE to the Next Level
As a leading supplier of BLE solutions, NXP has played a key role in helping
to add BLE to vehicles. In particular, our broad portfolio of BLE-enabled MCUs
is designed specifically for automotive use. Most recently, we’ve introduced
the
KW45, a third-generation device that delivers an unmatched combination of
security, flexibility, upgradability and performance.
Building on the success of the KW3x, the KW45 offers a three-core architecture
that includes a 96-MHz CM33 application core a dedicated CM3 64-MHz radio
core, and an isolated
EdgeLock Secure Enclave.
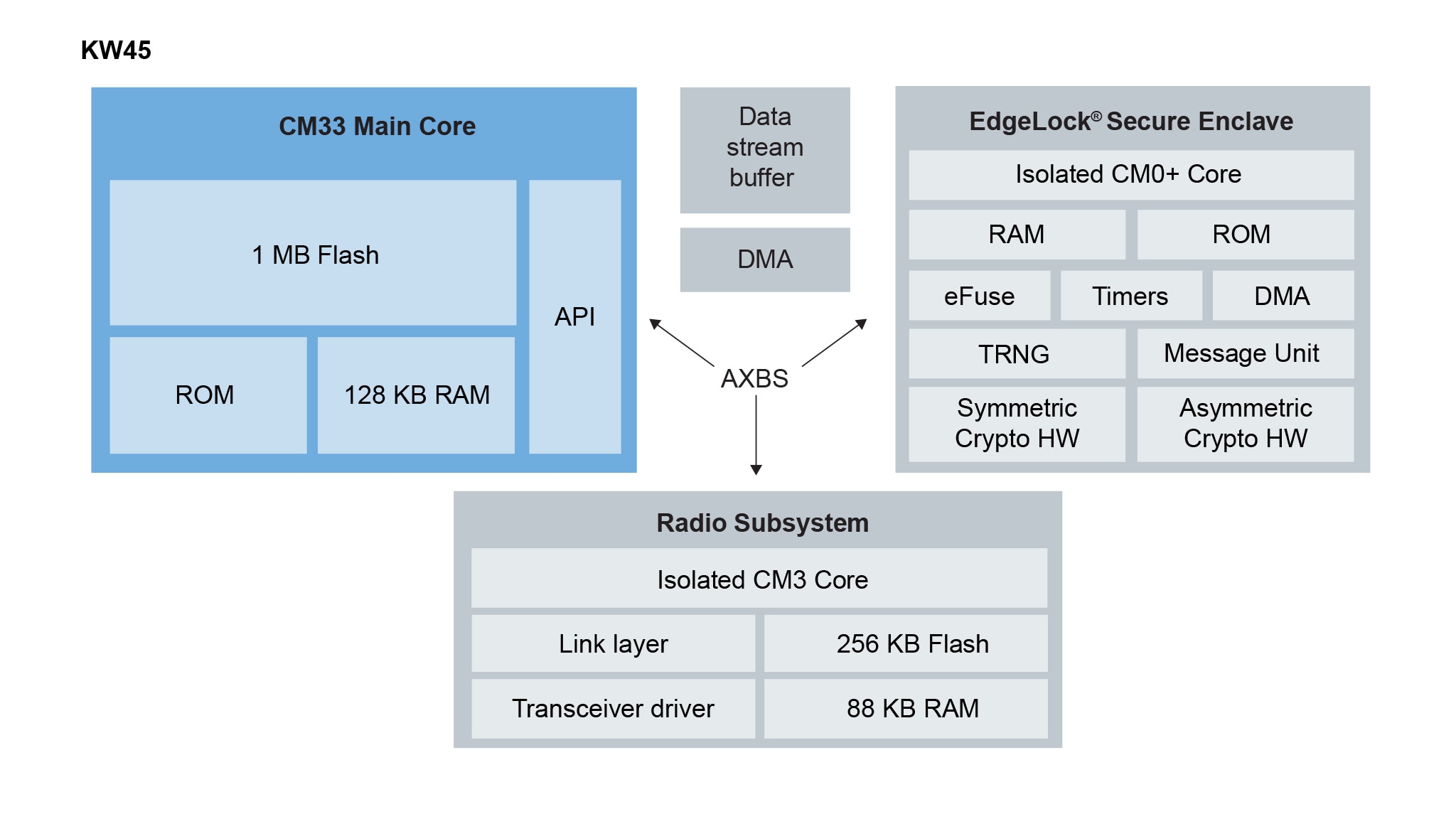 Use this block diagram to see the interaction between the three cores in the
KW45.
Use this block diagram to see the interaction between the three cores in the
KW45.
-
App core: 1 MB of Flash and 128 kB of RAM to support advanced automotive
applications, including communication over CAN, using an integrated FlexCAN
module, as well as support for AUTOSAR® applications.
-
Radio subsystem: Upgradeable Bluetooth 5.3 compliant, channel
sounding-capable radio core with 256 kB of Flash memory and up to 88 kB of
RAM.
-
EdgeLock Secure Enclave: Isolated core with advanced security features such
as secure lifecycle management, key-store operations and
hardware-accelerated cryptographic functionality.
By dividing responsibilities between application, radio and security cores,
the KW45 ensures that connected automotive applications have the resources,
upgradability and integration to evolve with changing standards and design
requirements.
NXP optimizes advanced Bluetooth solutions for multiple applications.
Enhance your design with NXP
Automotive or
Industrial Bluetooth solutions.
The KW45’s advanced hardware is supported by a suite of software-enablement
tools that target important automotive applications, including car sharing,
sensors, wireless on-board diagnostics functions and, of course, CCC Digital
Key 3.0 for secure car access. The KW45 is also the first to offer MCAL
drivers and a complex device driver for BLE enabling AutoSAR-compliant
solutions.
KW45 for Digital Key
The KW45 is designed to meet the advanced security requirements of Digital Key
3.0. The KW45’s EdgeLock Secure Enclave enables secure trust provisioning and
secure firmware updates, security lifecycle management and other security
tasks associated with secure access. For Digital Key 3.0, the KW45 enables BLE
with end-to-end security, so communications between the phone’s Secure Element
and the car’s Secure Element are always protected.
As part of a Digital Key 3.0 solution, along with
NXP’s Secure Elements
and
NFC product families, the KW45 works seamlessly with NXP’s Trimension SR106, the industry’s first
single-chip solution to combine UWB ranging and radar. Together, the KW45 and
SR106 create a single-supplier solution that simplifies the design of Digital
Key features. At the same time, the SR106 can do double duty, supporting
in-cabin radar, as part of occupant-safety systems now being mandated in
Europe, the US and elsewhere.
KW45 for AUTOSTAR-Certified ECUs
To streamline the development of automotive software and enable quick AUTOSAR
certification for electronic control units (ECUs), the KW45 includes an NXP
MCAL driver, which maps all the on-chip MCU peripheral modules and external
devices to memory and makes the upper software layer independent of the MCU.
KW45's MCAL driver package includes a complex device driver (CDD) for BLE. The
KW45 can also be combined with NXP’s SBC offerings, for a streamlined,
single-supplier solution for a broad range of ECU applications.
KW45 for Future-Proof Development
Using a Flash-based software core for radio operation adds a remarkable amount
of flexibility and longevity to the design. The KW45 can evolve as BLE
evolves, so vehicles can interface with smartphones today, tomorrow and for
years to come—without expensive, time-consuming hardware upgrades or
redesigns.
Near-field communication (NFC)
provides the backup entry for access when a smartphone runs out of power.
Altogether, these smart technologies function collectively to give users a
seamless experience.
Learn More
BLE can, in many ways, be seen as a megatrend in automotive design. At NXP,
we’re committed to delivering advanced BLE connectivity, with the advanced
capabilities, for vehicles of all kinds. The multi-core KW45, with its support
for digital-key standards from CCC and ICCE, as well as other advanced BLE use
cases, is the latest example of that commitment. Learn more about the
third-generation Bluetooth LE solution that is the
KW45.





